A Cruel Man Delighting in Flowers
...the mildness to which men ... had yielded was only half of the intoxication of beauty, while the other half ... was of such surpassing and terrible cruelty—the most cruel of men delights himself with a flower—that beauty ... failed quickly of its effect...
Hermann Broch, The Death of Virgil
Jeremy Davies is made of ink, but don’t dip a feather in him. It tickles. He once painted a fingernail black and no one really noticed. He was disappointed. He’s also an editor, a religious atheist, a liker of strong coffees, a Shakespeare-lover, a political anarchist and someone who rarely has a pen when he needs one. He has been a PhD candidate, a personal trainer, a life model, a bouncer, an infantry soldier and someone who rarely had a pen when he needed one. He has had words published in a variety of places, in a variety of publications, in a variety of forms, in a variety of moments: Canada, Wet Ink, SMS and twelve minutes past three in the afternoon being some of these. His first novel, 'Missing Presumed Undead', will be re-published by Satalyte Publishing in February 2014. A second is on its way.
Fellowship with the Defeated: Camus' 'The Plague'

1913–2013 A hundred years of Albert Camus, a writer.
…and to state quite simply what we learn in a time of pestilence: that there are more things to admire in men than to despise.
Yes, Nazism influenced the writing of this story, Camus was living through it and resisting it, in his way; but it is not about it. This novel, published after The Myth of Sisyphus and written during the sometimes hostile response to the book, begins what became to be known as Camus’ ‘Cycle of Revolt’ (along with The Rebel and the plays L'état de siege and Les justes). It is of interest to note that one of the regular complaints regarding Camus’ series of essays (notice, I do not say ‘Book of Philosophy’, which he never did…) of The Myth of Sisyphus—by both Camus’ contemporaries and thinkers today—is that it is ‘too abstract’ to be taken as a serious philosophical tract. The journalist, Rambert, echoes them when he says to Doctor Rieux:
”You’re using the language of reason, not of the heart; you live in a world of … of abstractions.”
In response, Rieux later muses to himself:
Yes, an element of abstraction, of a divorce from reality, entered into such calamities. Still, when abstraction sets to killing you, you’ve got to get busy with it.
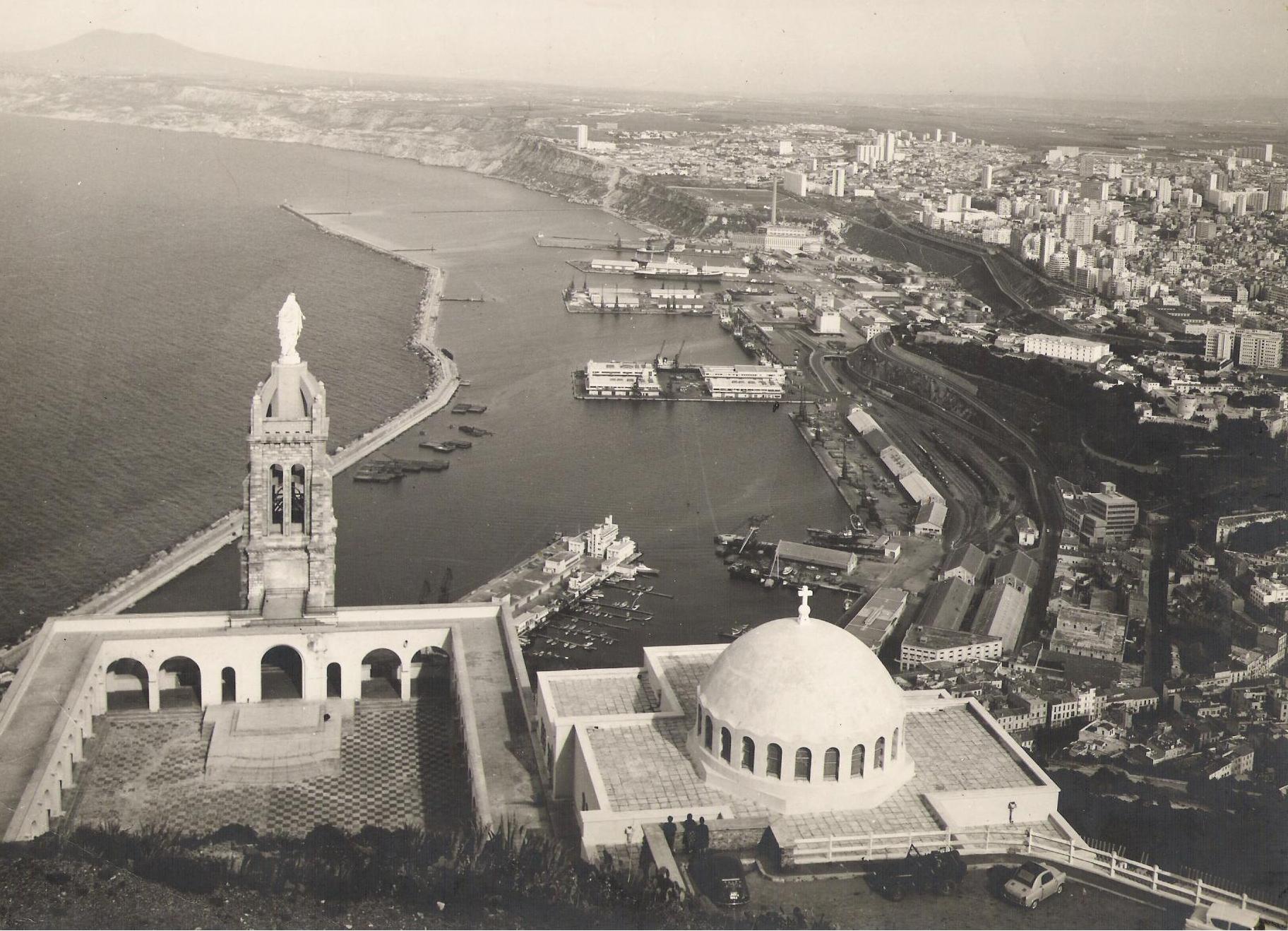

In this story, a city in North Africa, Oran, where Camus had lived for short amounts of time, becomes quarantined due to an outbreak of bubonic and, later, pneumonic, plague. Lots of people are dying and everybody has to deal with it, in their way. We follow the responses most closely of a Doctor (Rieux), a journalist (Rambert), a writer (Grand), an intellectual … for want of a better word (Tarrou), a priest (Paneloux) and a criminal (Cottard). Also of note is ‘the asthma patient’ that Rieux treats at key points in the narrative (in particular, right at the starts of the plague and right at the end. Why? Because his lung condition is mirroring Camus’ own (tuberculosis)—he required frequent treatments from Doctors, like Rieux—and it’s important to note that Camus’ often considered himself on the verge of death due to his condition, mirroring the psychology of those living with the plague: to live with the knowledge of the threat of imminent and unavoidable death.
‘They’re coming out, they’re coming out..’
He says gleefully. And later, at the end, he poses an important rhetorical question that’s been foreshadowed throughout the story:
”But what does that mean—‘plague’? Just life, no more than that.
And Tarrou, much later:
”…I had plague already, long before I came to this town.”
No, not Nazis, but life; but more specifically, life being brought into sharp focus, creating an awareness of it through an understanding that it ends. Being forced into exile by the plague, or not, the absurd conditions of life remain unaltered. It’s the awareness of the conditions that shifts through plague-caused exile: to be separated from the rest of the world, from love, from culture, etc; for it to be a part of your consciousness, and the consciousness of all the exiles around you, this is the plague. What does this do the people? It drives out Hope. It makes them live only in the past (through memories) and the present (through knowledge). The future no longer exists. Your illusions regarding your existence have flown. You have no peace.
This is the plague. The awareness of the absurd.
The only option is revolt; even in the face of the unchangeable.
And through this it’s possible, maybe not to be a saint, but to be a man.
…it was only right that those whose desires are limited to man, and his humble yet formidable love, should enter, if only now and again, into their reward.
How these characters come to terms with the plague and, thus, the Plague, forms the bulk of the story; and how they all, in different ways, follow Rieux’s lead and accept revolt, forms its chief intellectual interest. Without wanting to give away serious plot points, think about this when one of them contracts both varieties of plague—bubonic and pneumonic—the first person ever to do so…
Don’t get me wrong: this is also an aesthetic achievement of the highest order, even in translation: the scene with the dying boy reaches the aching terrible narrative beauty of one of Camus’ greatest literary heroes, Dostoevsky. But, indulge me in discussing some of these characters and how they played out in a kind of general sense, if you will…
Tarrou and Rieux have the most special relationship: the moment of ‘respite’ they share swimming alone at night in the forbidden sea is memorable to both of them, and to the reader. Just before hand, in conversation with Rieux, Tarrou comes to his main point about his life:
”It comes to this,” Tarrou said almost casually, “what interests me is learning how to become a saint.”
”But you don’t believe in God.”
”Exactly. Can one be a Saint without God?”
A little later on, Rieux finally responds:
”But, you know, I feel more fellowship with the defeated than the saints. Heroism and sanctity don’t really appeal to me, I imagine. What interests me is—being a man.”
”Yes, we’re both after the same thing, but I’m less ambitious."
Seeking sainthood is its own variety of retreat from the plague, not revolt. It’s full acknowledgement that the plague is greater-than. While Tarrou obsesses over existential issues, and broad morality, in his efforts to not transmit the plague to others, he can’t help but do so anyway. 
Paneloux, the priest, and Rieux clash on the other side of the plague. When Paneloux is introduced into the story, it is early days in the plague: people are seeking the solace of the Church, and he delivers his First Sermon, which is your typical ‘this is God’s vengeance upon his misbehaving creation’ kind of fare. Rieux is unimpressed. However, he asks Paneloux to become involved in the Santization Groups and he accepts, throwing himself into the actions of the revolt against the plague. After the death of the boy scene, there is a shift in his beliefs, and his Second Sermon follows that event. For those who have read The Brothers Karamazov...
(if you have not, what are you doing reading this rubbish review? Stop it and go out and read this book instead… No, wait, there’s time, as long as you don’t have plague: finish my review first…)
...this sermon could be read as how Aloysha should have responded to Ivan Karamazov when the death of innocents was put toward him as a reason to revolt against God (Book V, Ch. IV). Rieux summarises Ivan’s position nicely:
”And until my dying day I shall refuse to love a scheme of things in which children are put to torture.”
Instead of Aloysha’s quiet wishy-washy acceptance (coupled with his refusing to face the outcome of this acceptance) … a little like modern Western Christianity generally … Paneloux responds:
”Believe everything so as not to be forced to deny everything.”
”…they must acquire and practice the greatest of all virtues: that of the All or Nothing.”
He’s not saying that you’re either for God or against Him, but that you’re either with God or without Him. It’s no good being with Him when without plague, and without when you are. Because then you are without him anyway.
Rambert is the lover who wants to run from the plague. But comes to his own absurd realization.
Cottard finds the plague-stricken world better than the normal world.
Grand, the writer, revolts with the rest of them, but his life remains disturbingly unaffected. He obsesses over his opening sentence, which he’s been working on for years, mirroring Camus’ obsession with his book, which took him longer to write than any other. When Rieux gets a look at the full manuscript Grand is working on he notices that:
The bulk of the writing consisted of the same sentence written again and again with small variants.

In the end, even during the victory celebrations, the plague’s there, laying dormant, never really gone, waiting, even on ‘the bookshelves.’
Read this book. Get the plague.